Solar Power: Complete Guide to Renewable Energy, Benefits, and Real-World Applications
Solar power has become one of the most influential renewable energy solutions in the modern world. By converting sunlight into usable electricity, it offers a clean, sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. With the growing urgency to combat climate change and reduce carbon emissions, solar power is no longer just an option but a necessity for the future.
Harnessing solar power involves technologies that capture sunlight and transform it into electricity or heat. The most common method is through solar panels, which use photovoltaic (PV) cells to generate direct current (DC) electricity. This electricity is then converted to alternating current (AC), making it suitable for powering homes, businesses, and even entire communities.
How Solar Power Works
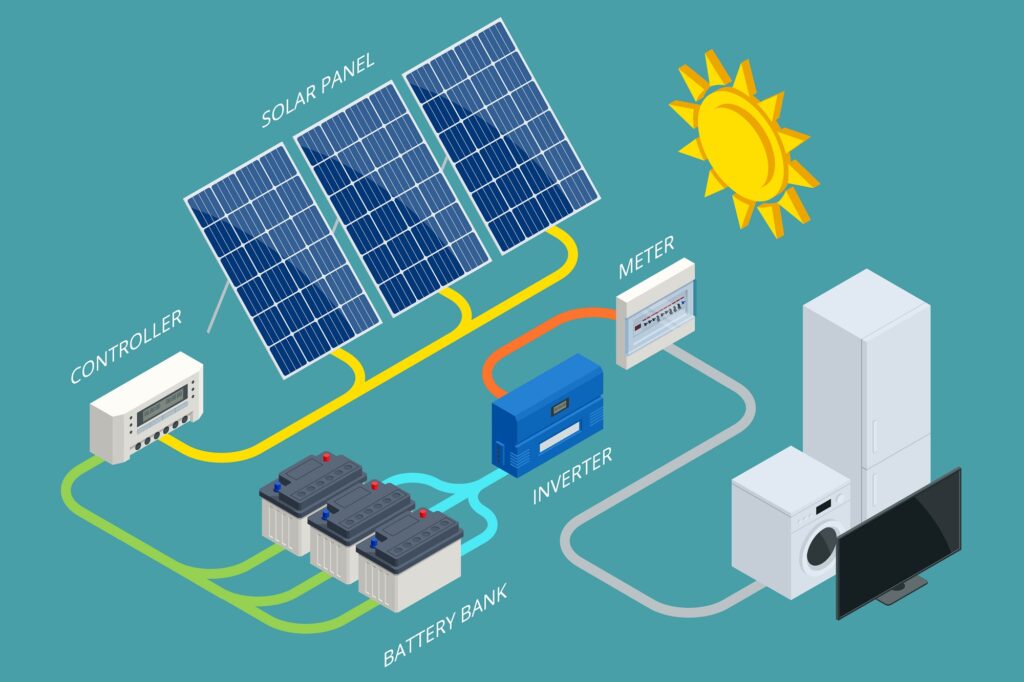
Solar power systems operate on the principle of the photovoltaic effect. When sunlight strikes a solar cell, it excites electrons, creating an electrical current. These cells are grouped into panels, which can be installed on rooftops, open fields, or integrated into building structures.
Beyond PV panels, solar power also includes concentrated solar power (CSP) systems, which use mirrors to concentrate sunlight and produce heat. This heat is then used to drive turbines and generate electricity, much like conventional power plants, but without burning fossil fuels.
The versatility of solar power technologies means it can be adapted for small-scale residential use, large-scale commercial projects, or even utility-scale power generation.
Benefits of Solar Power Technology
Solar power offers a wide range of benefits for individuals, businesses, and society as a whole. One of the most significant advantages is sustainability. Solar energy is renewable and abundant, providing a virtually limitless supply of clean power as long as the sun shines.
Another benefit is energy independence. By installing solar systems, homeowners and businesses can reduce their reliance on utility companies and shield themselves from fluctuating energy costs. This independence is particularly valuable in regions with unstable electricity supplies.
Additionally, solar power reduces carbon emissions, helping to mitigate climate change. Unlike fossil fuels, solar panels generate electricity without releasing greenhouse gases, making them a vital component of global clean energy strategies.
Solar technology also provides long-term economic value. While initial setup costs can be significant, the long lifespan and low maintenance requirements of solar systems often result in substantial savings over time.
Real-World Examples of Solar Power Solutions

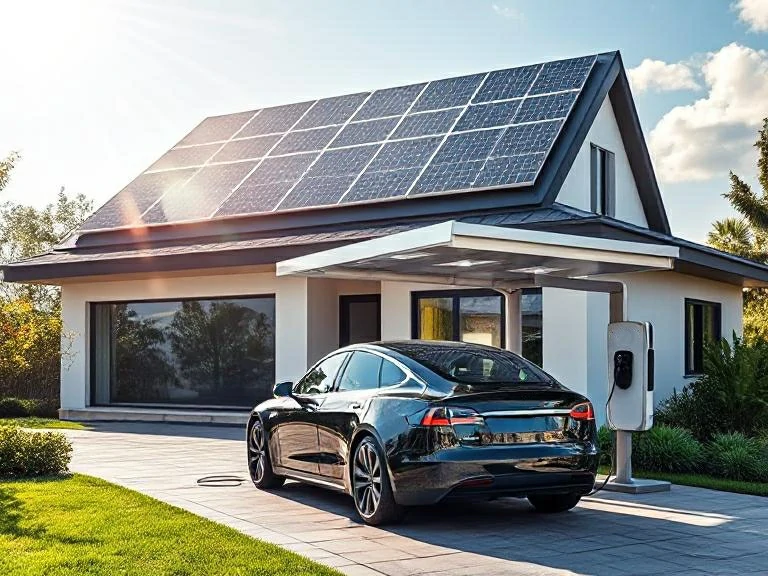
Tesla Solar Roof
Tesla Solar Roof is a groundbreaking product that integrates solar cells directly into roofing tiles. Unlike traditional panels, these tiles serve both as a roof and an energy-generating system.
The relevance of Tesla Solar Roof lies in its combination of functionality and aesthetics. Homeowners can enjoy the benefits of solar energy without compromising the appearance of their property. It represents the future of building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV).
SunPower Maxeon Solar Panels
SunPower Maxeon panels are known for their industry-leading efficiency, durability, and long-term performance. Their copper-backed cells prevent corrosion and ensure reliability even in harsh conditions.
The relevance of SunPower Maxeon panels is their high energy yield per square foot, making them ideal for rooftops with limited space. They provide consistent energy production, ensuring long-term sustainability and cost savings.
SolarEdge Smart Energy Solutions
SolarEdge offers advanced inverter and energy optimization solutions for solar power systems. Their technology maximizes energy production by allowing each panel to operate independently, even in partially shaded conditions.
The relevance of SolarEdge lies in its focus on efficiency and monitoring. With real-time data and optimization, homeowners and businesses can ensure they are getting the maximum return on their solar investment.
First Solar Utility-Scale Panels
First Solar is a leader in utility-scale solar projects. Their thin-film solar modules are designed for large installations and provide strong performance in hot and humid climates.
The relevance of First Solar is its contribution to large-scale renewable energy production. These panels are often used to power entire communities or contribute to national grids, reducing dependence on fossil fuels on a massive scale.
LG NeON Solar Panels
LG NeON panels are built for efficiency, performance, and long lifespan. They use advanced cell technology to generate more electricity from the same amount of sunlight.
The relevance of LG NeON panels is their reliability and proven track record in residential installations. They help families significantly cut energy bills while supporting a cleaner environment.
Practical Benefits of Solar Power in Daily Life
In daily life, solar power translates into practical advantages for households and businesses. For homeowners, it reduces monthly electricity bills and provides stability against rising utility prices. Families can also enjoy uninterrupted power during outages when paired with battery storage.
Businesses benefit from solar power through lower operational costs and improved corporate sustainability. Installing solar systems enhances brand reputation by demonstrating commitment to environmental responsibility, which can also attract eco-conscious customers.
Another key benefit is the low maintenance requirements of solar systems. Once installed, panels require minimal upkeep, often limited to occasional cleaning and inspections, making them convenient for long-term use.
Use Cases: Problems Solar Power Solves

Solar power directly addresses the problem of energy scarcity. In regions with unreliable power grids, solar systems provide consistent electricity for homes, schools, and hospitals, improving the quality of life and economic development.
It also solves the issue of rising energy costs. By generating electricity on-site, solar users can reduce or eliminate utility bills and protect themselves from unpredictable rate hikes.
Another major use case is disaster resilience. In areas prone to storms, earthquakes, or grid failures, solar systems combined with storage provide critical backup power for essential services.
Finally, solar power tackles the global challenge of climate change. By replacing fossil fuel energy with clean, renewable alternatives, solar contributes significantly to reducing greenhouse gas emissions worldwide.
Challenges and the Future of Solar Power

Despite its advantages, solar power faces challenges. The initial installation cost can be high, making it less accessible for some households or businesses. Additionally, solar generation is dependent on sunlight, meaning energy output can vary with weather and seasonal changes.
However, the future of solar power is bright. Advances in panel efficiency, battery storage, and grid integration continue to make solar more affordable and reliable. Governments and organizations around the world are also investing heavily in solar infrastructure, ensuring it plays a central role in the global transition to renewable energy.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How long do solar panels last?
Most solar panels last between 25 and 30 years, with many continuing to produce electricity beyond their warranty period. Their performance may gradually decline, but they remain effective for decades.
2. Can solar power work during cloudy days?
Yes, solar panels can still generate electricity on cloudy days, though output will be lower compared to sunny conditions. Advanced panels are designed to perform well even in low-light environments.
3. Is solar power suitable for all types of homes?
Solar power can be adapted for most homes, but factors such as roof size, orientation, and shading can influence performance. Professional assessment helps determine the best system design for each property.




