Solar Panels: Comprehensive Guide to Benefits, Technology, and Real-World Applications
Solar panels are devices that convert sunlight into electricity, providing a clean, renewable source of energy. They are primarily made of photovoltaic (PV) cells, which absorb photons from sunlight and release electrons to generate an electric current. This process, known as the photovoltaic effect, forms the foundation of solar energy technology.
Over the years, solar panels have evolved into highly efficient systems that can be installed on rooftops, fields, or even integrated into building materials. They serve residential, commercial, and industrial purposes, reducing dependence on fossil fuels and helping combat climate change.
Types of Solar Panels

Solar panels come in different types, each with unique properties. Monocrystalline panels are made from a single crystal structure and are known for their high efficiency and sleek appearance. Polycrystalline panels, created from multiple crystal fragments, are slightly less efficient but more cost-effective. Thin-film solar panels, made from lightweight layers of semiconductors, are flexible and ideal for unconventional surfaces.
Each type of solar panel has its own strengths, and the choice often depends on available space, budget, and desired efficiency. Advances in solar technology continue to enhance performance and broaden applications, making solar energy more accessible worldwide.
Benefits of Solar Panels
One of the most significant benefits of solar panels is their ability to generate clean energy. Unlike fossil fuels, which release greenhouse gases, solar panels harness renewable sunlight, significantly reducing carbon emissions. This contributes to global efforts to mitigate climate change and protect ecosystems.
Economically, solar panels offer long-term savings. While the initial investment can be high, the reduction in electricity bills and the longevity of panels, often lasting 25 years or more, make them cost-effective over time. They also add value to properties, making solar-powered homes and businesses more attractive in the market.
Another benefit is energy independence. By generating their own power, homeowners and businesses become less vulnerable to rising energy costs and power outages. Solar panels also support decentralized energy systems, reducing strain on the grid and improving resilience in communities.
Real-World Examples of Solar Panel Applications

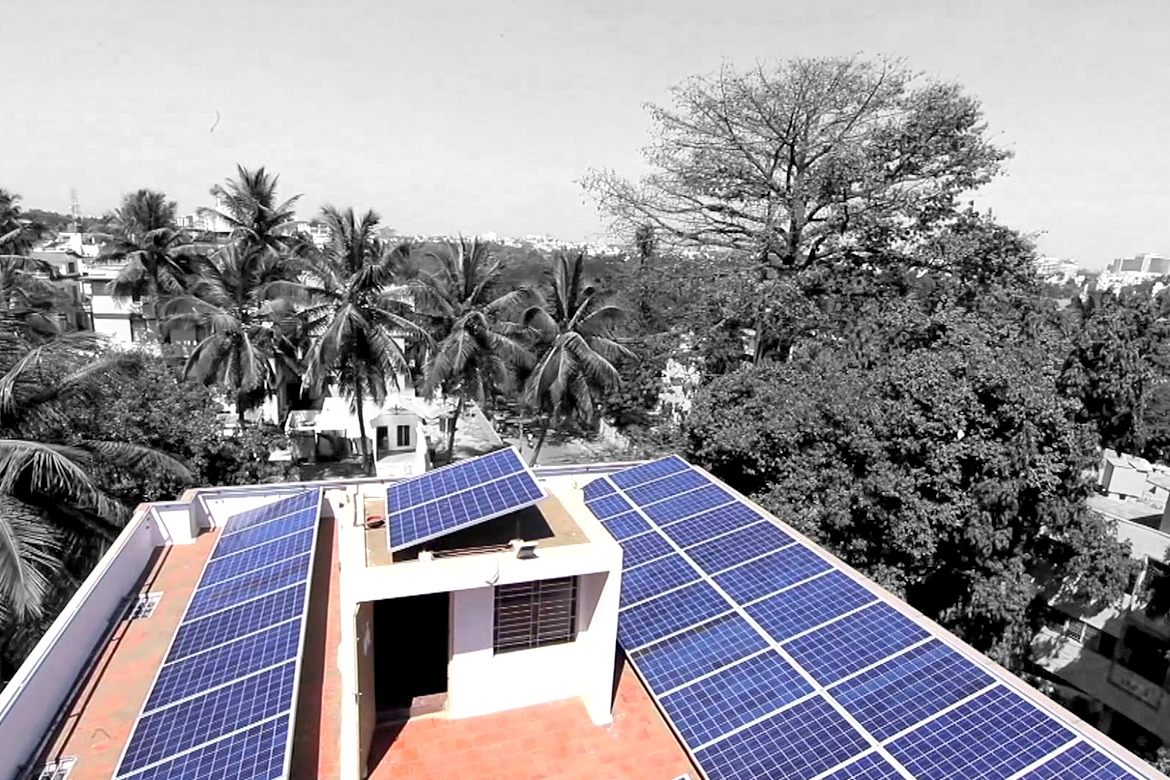
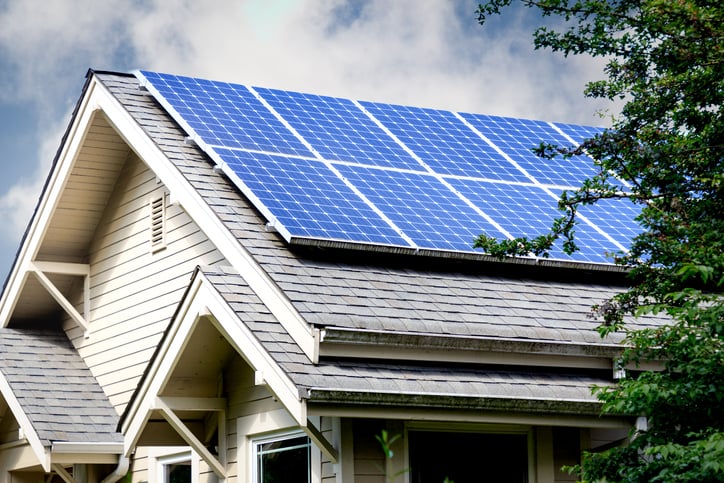
Residential Rooftop Solar Systems
Rooftop solar panels are among the most common applications, especially in residential areas. Homeowners install panels on rooftops to generate electricity for daily use, often paired with energy storage systems to ensure a continuous supply.
These systems allow households to significantly reduce their electricity bills while contributing to sustainability. In some regions, excess electricity can even be fed back into the grid, creating an additional advantage. Rooftop solar represents a practical and scalable solution for clean energy adoption at the individual level.
Solar Farms
Solar farms, also known as photovoltaic power stations, are large-scale installations designed to supply electricity to thousands of households or businesses. They are usually built in open fields with optimal sunlight exposure and consist of thousands of interconnected panels.
These projects play a key role in national energy strategies, replacing coal or gas plants with renewable sources. Solar farms demonstrate how solar technology can be scaled to meet the energy demands of entire communities, reducing reliance on fossil fuels at a macro level.
Floating Solar Panels
Floating solar panels are an innovative solution for areas with limited land availability. Installed on bodies of water such as reservoirs, lakes, or ponds, they maximize unused space while minimizing land competition.
Beyond electricity generation, floating solar panels reduce water evaporation and improve panel efficiency by staying cooler on water surfaces. This dual functionality makes them highly effective in water-scarce regions, combining energy production with resource conservation.
Solar-Powered Schools and Hospitals
Educational and healthcare institutions increasingly adopt solar panels to reduce operational costs and ensure reliable energy. Schools benefit from lower energy bills, allowing them to allocate more funds to educational programs. Hospitals, which require uninterrupted power, gain resilience against blackouts and reduce their carbon footprint.
These applications highlight the social dimension of solar panels, proving their role in empowering communities by providing sustainable and reliable energy solutions where they are most needed.
Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV)
BIPV involves integrating solar panels directly into building materials such as facades, roofs, or windows. This approach allows architects to design structures that generate energy without compromising aesthetics.
BIPV systems reduce construction material use while providing renewable energy generation. They represent the future of urban solar applications, blending sustainability seamlessly into architectural design.
Practical Use Cases of Solar Panels

Solar panels solve several real-world challenges. In rural areas without access to electricity grids, solar panels power homes, schools, and healthcare centers, bridging the energy gap. This supports development, education, and healthcare delivery in underserved communities.
In disaster-prone regions, solar panels provide critical backup energy when conventional power infrastructure fails. For businesses, solar panels reduce operating costs and ensure predictable energy expenditures, shielding them from volatile fossil fuel markets.
Solar panels are also used in agricultural applications, powering irrigation systems, water pumps, and refrigeration units for crops. These uses increase productivity while reducing dependency on non-renewable energy sources, improving sustainability in farming practices.
Long-Term Advantages of Solar Panels

The long-term value of solar panels extends far beyond cost savings. They are a cornerstone of global energy transitions, helping countries achieve renewable energy targets and reduce dependence on fossil fuels. Solar panels also foster innovation, driving research in storage technologies, efficiency improvements, and smart grid integration.
At the household and business level, solar adoption improves property value, enhances energy security, and promotes resilience. From a global perspective, widespread solar panel use is critical to achieving carbon neutrality and ensuring a sustainable future for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main types of solar panels?
The three main types are monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film. Each type has unique characteristics, with monocrystalline panels being the most efficient, polycrystalline panels offering a balance of cost and performance, and thin-film panels providing flexibility.
Do solar panels work during cloudy days or at night?
Solar panels generate less electricity during cloudy days but still produce some power. At night, they do not generate energy; however, pairing them with storage systems like batteries ensures a steady supply of electricity around the clock.
How long do solar panels last?
Most solar panels last between 25 and 30 years. Their efficiency gradually decreases over time, but with proper maintenance, they continue to produce electricity effectively for decades, making them a long-term investment in clean energy.